Confirmation
Hyperkalemia
Definition
Serum potassium > 5.5mEq/L, associated with lethal arrhythmias and hemodynamic compromise.
History/Physical Exam
Hx of renal failure, rhabdomyolysis, burns, potassium-sparing diuretics, NSAIDs, β-blockers.
Often presents with fatigue, weakness, or paresthesia. May present with paralysis, dyspnea, or chest pain.
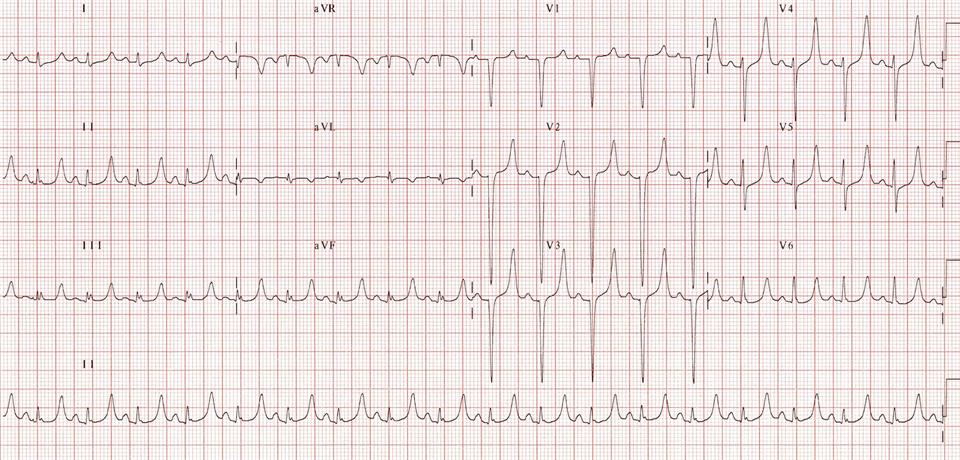
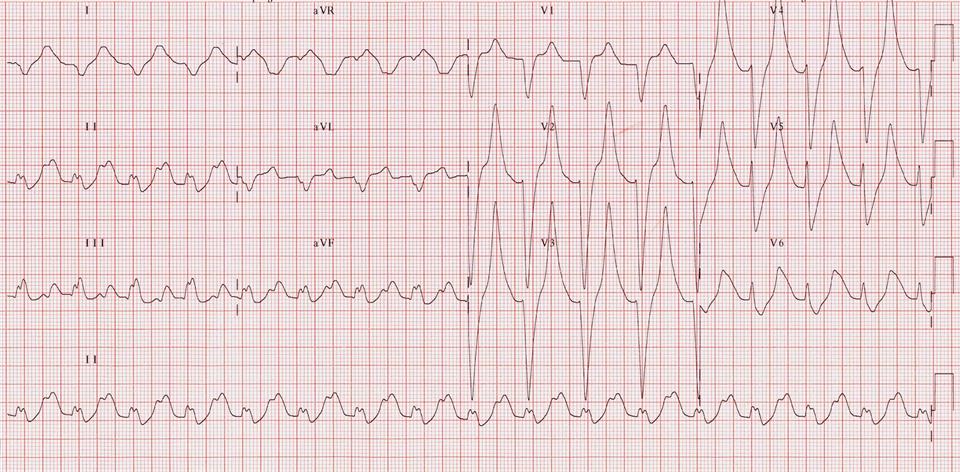
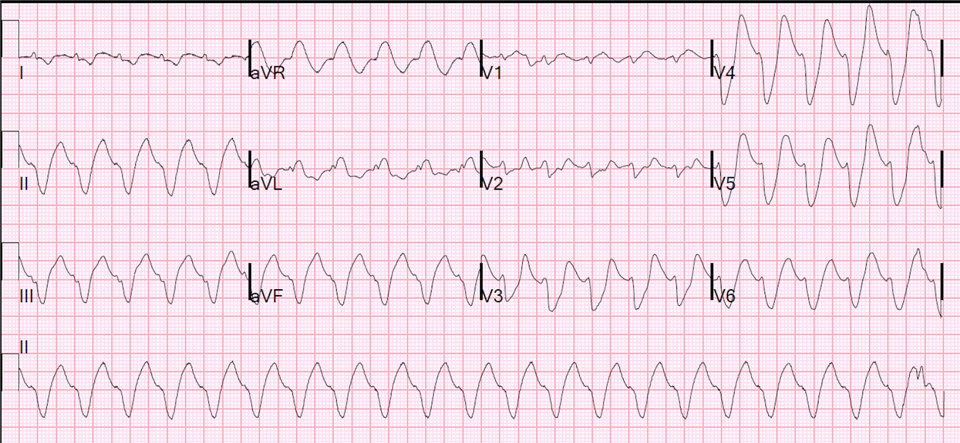
Key 12-Lead Features
Flattened P waves, prolonged PR intervals, borderline widened QRS complexes and pointed, narrow, and tall tented T waves.
May progress to bradycardia, bizarre and wide QRS complexes, or sine waves.
Key Treatment Points
If patient is in arrest, front-load with Calcium Chloride and Sodium Bicarbonate
Salbutamol - 10-20mg nebulized may reduce serum K+ 0.5-1.5mEq
12 Lead ECG Samples
References
Heidari, S. F. (2016). Life-Threatening Severe Hyperkalemia Presenting Electrocardiographic Changes. Journal of Intensive and Critical Care, 02(03). doi:10.21767/2471-8505.100045.