Confirmation
Pulmonary Embolism
Definition
A sudden blockage in an artery of the lung.
Wells Criteria for Suspected PE
| Criterion | Points |
| Clinically suspected DVT (pain with palpation, unilateral edema, varicose veins) | 3.0 |
| PE Diagnosis is as likely or more likely than another differential | 3.0 |
| Tachycardia (HR > 100/min) | 1.5 |
| Immobilization/Surgery (in last 4 weeks) | 1.5 |
| Previous DVT/PE | 1.5 |
| Hemoptysis | 1.0 |
| Malignancy (treated within last 6 months) | 1.0 |
| Score | Risk | Probability of PE | % of Patients with this Score |
| > 6 | High | 66.7% | 7% |
| 3-6 | Moderate | 20.5% | 53% |
| 0-2 | Low | 3.6% | 40% |
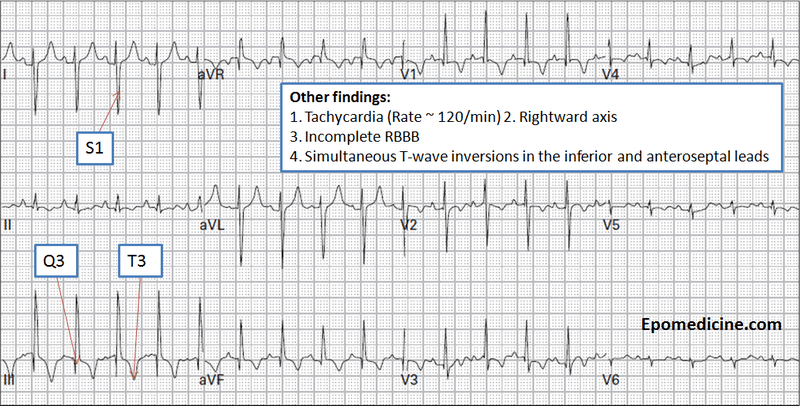
Key 12-Lead Features
Sinus tachycardia (73% sensitivity)
Prominent S-wave in Lead I (73%)
"Clockwise rotation" / late precordial transition (56%)
T-wave inversion in 2+ precordial leads (50%)
Incomplete or complete RBBB (20-68%)
P-pulmonale (28-33%)
Right axis deviation (23-30%)
No significant findings (20-24%)
S1Q3T3 (12-25%) (pressure overload of the right ventricle)
Key Treatment Points
Rapid conveyance to hospital, including in cardiac arrest
12 Lead ECG Samples
Reference
Stein PD, Woodard PK, Weg JG, Wakefield TW, Tapson VF, Sostman HD, Sos TA, Quinn DA, Leeper KV, Hull RD, Hales CA, Gottschalk A, Goodman LR, Fowler SE, Buckley JD (2007). "Diagnostic pathways in acute pulmonary embolism: recommendations of the PIOPED II Investigators". Radiology 242 (1): 15–21.