Confirmation
Download PDF
Long QT Syndrome
Definition
Prolonged QT interval; a propensity to ventricular tachy-arrhythmias, syncope, cardiac arrest, or sudden death.
History/Physical Exam
May be congenital or due to hypomagnesemia/kalemia (diuretics, malnourished), hypothermia, Rx (amiodarone, cipralex, methadone, etc). Family history of unexplained sudden death.
Presents with syncope from adrenergic stimuli - such as exercise, emotion, loud noise, swimming.
Key 12-Lead Features
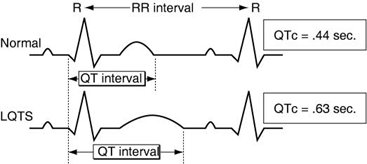
QTc > 0.46 (women)
QTc > 0.45 (men)
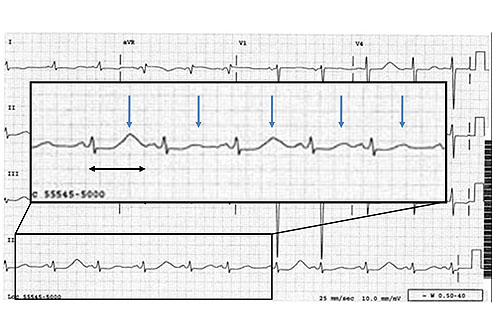
T-wave alternans
Key Treatment Points
Watch for Torsade de Pointes
If patient arrests, Magnesium Sulfate is indicated
12 Lead ECG Samples
Notice the T-Wave alternans below
References
El-Sherif, N., Turitto, G., & Boutjdir, M. (2017). Congenital Long QT syndrome and torsade de pointes. Annals of Noninvasive Electrocardiology. doi:10.1111/anec.12481.